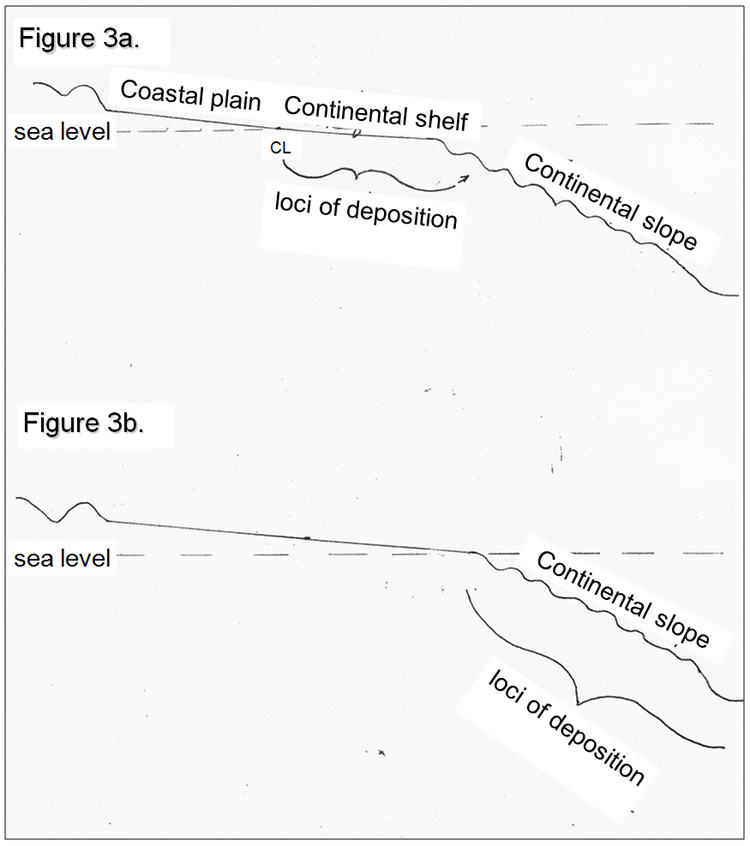
Figure 3. Massive short-term glacial-lake outburst depositions during lowstands generating low-frequency stress fields.
Figure 3a. During high sea-level stands, river-borne sediments reach the coastline with deposition occurring across the continental shelf. “Normal” river flowage rates ~ 104 m3/sec.
Figure 3b. During low sea-level stands in times of glacial advance, river-borne sediments reach the present-day shelf-break and continental slope with deposition across the continental slope. With the unusual (once every half century to multiples centuries) glacial-lake outbursts, the up to pea-sized gravel on the continental slope. “Normal” river flow rates of ~ 102 – 103 m3/sec are sufficient to create braided streams in the paleo-Red and Mississippi River valleys. CL = coastline.
